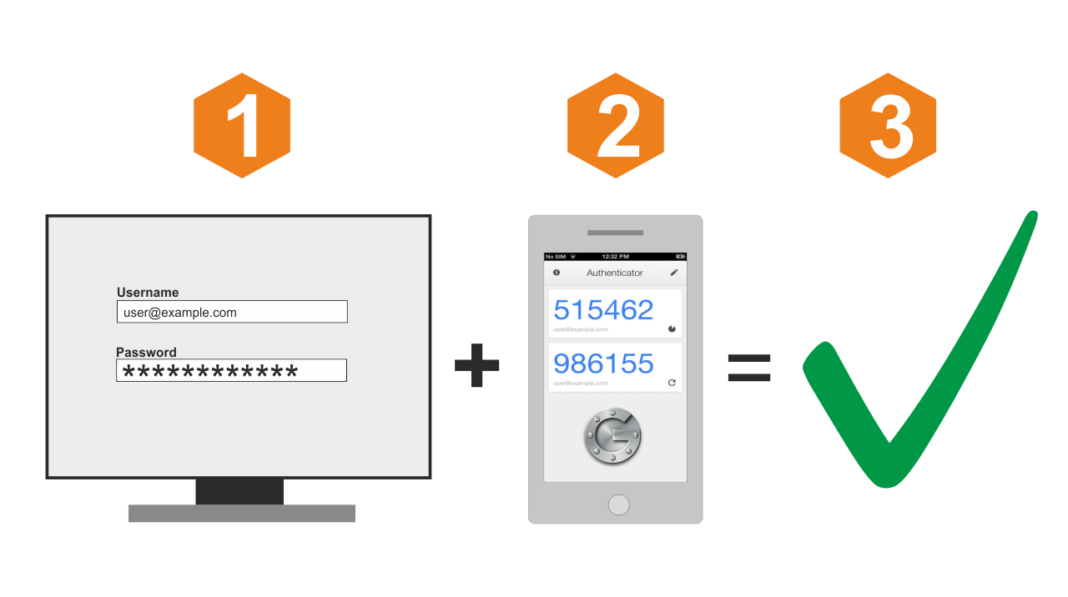
Two-factor authentication (2FA), also known as Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), is a security measure that requires two separate ways of proving your identity before accessing an online accounts. This process is designed to add an extra layer of protection to sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access, even if the password has been compromised.
In this post, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to set up 2FA for some popular online services and platforms.
Step 1: Determine which services support 2FA
The first step in setting up 2FA is to determine which online services and platforms you use that offer this security feature. Some of the most popular ones include:
- Google (for Gmail, Google Drive, etc.)
- Apple (for iCloud, iTunes, etc.)
- Microsoft (for Outlook, Skype, etc.)
- Dropbox
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Step 2: Choose a 2FA method
Once you have identified the services you use that support 2FA, the next step is to choose a 2FA method that works best for you. The most common methods include:
- SMS text messages: A code is sent to your phone via text message, which you enter on the website to confirm your identity.
- Authenticator apps: An app installed on your smartphone generates a unique code that you enter on the website. The two best ones are Microsoft Authenticator and Google Authenticator App.
- Security keys: A physical device that you plug into your computer or connect wirelessly to confirm your identity.
Step 3: Enable 2FA on each service
The process for enabling 2FA on each service may vary, but the steps are generally similar. Here’s an example for setting up 2FA on Google:
- Log into your Google account and navigate to the Security section.
- Scroll down to the Two-step verification section and click on Get started.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to verify your phone number and choose the 2FA method you prefer.
- Download and install the Google Authenticator app on your smartphone if you have chosen to use it.
- After enabling 2FA, you will need to enter a verification code each time you log in to your Google account.
Step 4: Store backup codes
It’s important to store backup codes in a secure location, in case you lose access to your smartphone or the 2FA app. To obtain backup codes, follow these steps:
- Log into your Google account and navigate to the Security section.
- Scroll down to the Two-step verification section and click on Setup backup codes.
- Print or save the backup codes in a secure location.
Step 5: Update your recovery information
It’s a good idea to update your recovery information, such as a secondary email address or phone number, in case you lose access to your 2FA device or need to recover your account. To update your recovery information, follow these steps:
- Log into your Google account and navigate to the Security section.
- Scroll down to the Recovery information section and click on Edit.
- Update your recovery information as needed.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication is a simple but effective way to protect your online accounts and sensitive information. By following these steps, you can ensure that your data is secure and only accessible by you. Additionally, it’s important to regularly review and update your 2FA settings and recovery information to ensure they remain current.
It’s important to remember that 2FA is not foolproof, and it’s still necessary to follow best practices for password management, such as using strong and unique passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi, and being mindful of phishing scams.
It’s also essential to keep your 2FA information and backup codes up-to-date and stored in a secure location. Regularly reviewing and updating your 2FA settings will help ensure that your accounts remain secure.
In this digital age, data security has become more important than ever, and 2FA is one of the most effective ways to protect your online presence. By following this guide, you can ensure that you have taken the necessary steps to secure your accounts and keep your information safe.